Kalmar ($KALM) Review: An Impartial Analysis of Its Legitimacy, Security, and Risks
Project Overview
Kalmar, operating under the ticker $KALM, presents itself as a multifaceted decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem built primarily on the Binance Smart Chain (BSC) and extending its cross-chain ambitions into Fantom and Avalanche networks. The platform aims to unify a suite of DeFi primitives—including yield farming, token swaps, NFT staking, liquidity pools, and governance—within an integrated marketplace that emphasizes user-friendly interfaces, low transaction costs, and cross-chain interoperability.
This review offers an objective and evidence-based assessment of Kalmar’s core elements, examining its technological foundations, security posture, economic model, and strategic risks. Given the dynamism of DeFi projects, this analysis balances its innovative claims against practical vulnerabilities, audit transparency, and long-term viability.
Team and Roadmap Evaluation
The available data indicates that Kalmar’s development team is currently anonymous, a common trait among blockchain projects aiming to prioritize decentralization or privacy. The lack of publicly disclosed founders or core team bios warrants caution, as transparency around team experience and track record can significantly influence perceived credibility. For guidance on this, our article on strategies for verifying crypto team credibility can be beneficial.
The project’s roadmap highlights several functional modules: multi-chain token deployments, cross-chain liquidity pools, NFT staking platforms, leveraged yield farming mechanisms, and governance tools like voting and bonds. Key milestones include:
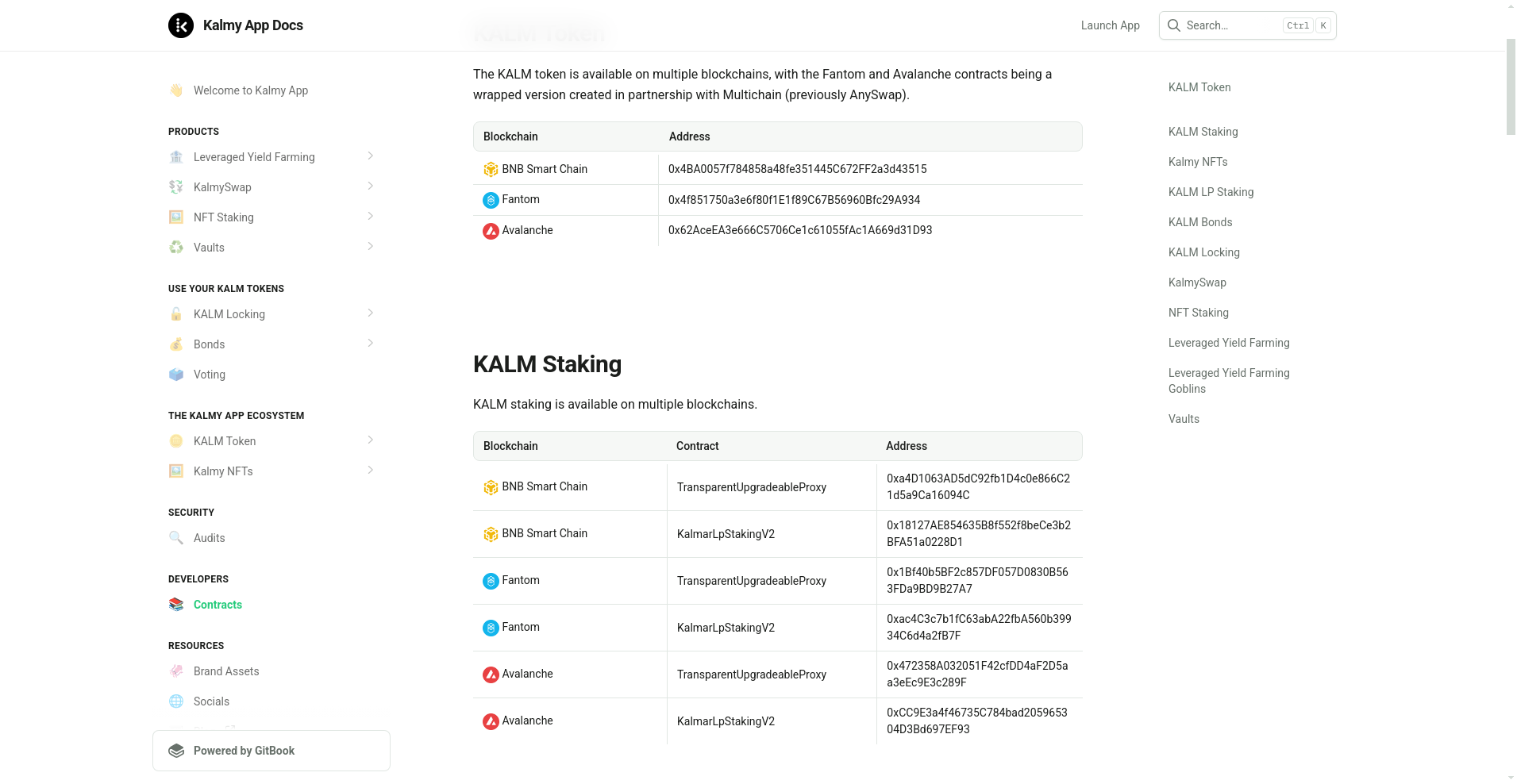
- Deployment of KALM on BSC, Fantom, and Avalanche.
- Introduction of NFT collections and NFT staking features.
- Launch of cross-chain liquidity pools and KalmySwap, the ecosystem’s AMM aggregator.
- Implementation of token locking, bonds, and governance voting modules.
However, the last available software update or public milestone appears to be over two years old, which raises questions about ongoing development or recent feature upgrades. The absence of recent public progress reports or updates suggests a potential stagnation or a gap in community engagement.
Security and Trust Analysis
Based solely on the publicly available audit reports from Hacken and PeckShield, Kalmar has undergone a total of four assessments spanning from April 2021 to April 2022. These audits include:
- Hacken’s audits (June 2021 and April 2021), focusing on smart contract security and overall protocol robustness.
- PeckShield’s audits (August 2021 and April 2022), with the latter specifically targeting bond modules.
The audits’ reports are publicly accessible via provided links, underscoring transparency. Nonetheless, the details of findings—such as identified vulnerabilities, severity ratings, or remediation steps—are not summarized in the documentation. This absence necessitates a review of the actual audit reports to verify whether critical flaws exist. For context on what to look for, consider our guide on evaluating crypto project transparency and communication.
Security awareness is further signaled by the presence of bug bounty programs and ongoing security assessments. However, without recent audits or disclosures of vulnerabilities, the project’s security maturity remains somewhat opaque. Investors should consider that multi-year-old audit reports may not reflect current security conditions, especially if smart contracts have undergone upgrades or new modules are added.
Tokenomics Breakdown
The KALM token supplies a total fixed quantity of 10 million tokens. Its distribution aims to balance incentives across ecosystem participants:
- Liquidity Mining: 59% allocated—indicating a heavy emphasis on incentivizing liquidity providers, which could drive short-term trading volume and liquidity depth.
- Private Round: 9%—likely reserved for initial investors or strategic partners.
- Partnerships: 9%—intended for ecosystem collaborations and integrations.
- Team: 8.5%—a modest allocation designed to align long-term incentives.
- NFT Fundraiser + IFO: 14.5%—funds raised through NFT sales and Initial Farm Offerings to grow ecosystem features.
The token is designed for multiple utilities—including locking for governance rights, participating in bonds, and staking. A notable feature is KALM’s multi-chain deployment with contract addresses across BNB Smart Chain (BNB Chain), Fantom, and Avalanche. The core tokenomics appear stable with a capped supply, but heavy liquidity mining-driven incentives can potentially lead to inflationary pressures if not carefully managed. Understanding potential liquidity enhancement strategies is crucial when assessing such models.
Economic sustainability hinges on continuous ecosystem growth, active governance, and proper reward rate adjustments to prevent excessive token issuance or disinflation. The absence of details on emission schedules, vesting, or burn mechanisms warrants further investigation.
Ecosystem and Development Activity
Data and community reports suggest Kalmar maintains a broad ecosystem encompassing:
- Cross-chain AMM aggregator (KalmySwap) supporting trades across BSC, Fantom, and Avalanche.
- NFT collections and staking mechanisms designed to promote community engagement and liquidity.
- Leveraged yield farming modules with multiple pools and token pairs. This strategy can be further refined by exploring advanced yield farming strategies with leverage.
- Bonds and governance voting features designed to decentralize decision-making and align incentives, which can be understood better through Kalmar's token locking and governance mechanics.
However, the last explicit updates or product releases date back more than two years, hinting at limited recent activity or a lack of transparent ongoing development. Interpretations vary: this could reflect a stable mature platform, or a stagnating project with dormant features. Nevertheless, the platform’s multi-chain presence and audit diligence are points in its favor, indicating a serious approach to ecosystem breadth.
Furthermore, the depth of documentation, resources, and user guides (covering wallet setup, token conversions, and staking) signals a focus on onboarding and community education, albeit with potential out-of-date content.
Reviewing the Terms and Conditions
The publicly available documentation does not explicitly detail legal terms, user agreements, or compliance disclosures. No specific clauses about user rights, jurisdiction, or potential legal risks are highlighted, which is common in DeFi projects that often operate in loosely regulated environments. However, the absence of transparency on legal frameworks underscores the importance of due diligence, especially given the anonymous team structure and multi-chain deployment.
Investors should be aware that DeFi protocols often carry contractual risks like smart contract bugs, liquidity issues, or governance disputes. The lack of recent formal legal terms in the documentation suggests a conservative stance or simply a need for external legal review before large-scale adoption.
Final Analysis: The Investment Case for Kalmar
Kalmar’s ecosystem appears comprehensive, integrating cross-chain liquidity, NFT staking, leveraged yield farming, and governance modules. Its deployment on multiple blockchains and auditable smart contracts provide a solid foundation. However, significant caveats include its anonymous team, outdated documentation (last updated over two years ago), and limited recent activity disclosures.
While the multiple security audits from reputable firms imply a baseline of safety, the absence of detailed findings and potential contract upgrades or ecosystem changes cast some residual doubt. Its heavy reliance on liquidity mining could introduce inflationary risks, especially if rewards are not adjusted appropriately over time.
In sum, Kalmar shows promise as a multi-product DeFi hub with innovative features like NFT incentivization and cross-chain swaps. Nevertheless, prospective investors should proceed with caution, verify current smart contract statuses, and critically assess whether ongoing development and security audits align with industry best practices.
-
Pros / Strengths
- Multi-chain deployment with cross-chain liquidity pools.
- Comprehensive ecosystem including NFTs, governance, bonds, and staking.
- Historical security audits by reputable firms.
- Transparent, public audit reports and exploits mitigate concerns.
- Focus on user onboarding with guides and educational resources.
- Decentralized governance potential via voting and token locking.
- Ambitious multi-product strategy targeting DeFi and NFT communities. Cons / Risks
- Anonymous team limits transparency and accountability.
- Documentation last updated over two years ago—possible out-of-date features or contract states.
- Audit reports lack detailed vulnerability status; on-chain verification needed.
- Heavy liquidity mining could create inflationary pressure or dumps.
- Limited recent development updates or active community signals.
- Potential technical complexity in cross-chain interoperability and upgradeability.
- Unclear how recent the deployed smart contracts are—possible multiple upgrades or unverified code.
In conclusion, Kalmar holds considerable potential as an integrated DeFi ecosystem with innovative cross-chain and NFT features. However, credible risk mitigation, up-to-date security assessments, and transparent project updates are necessary for it to be viewed as a trustworthy long-term investment.

David Martinez
Quantitative Risk Modeler
Quantitative analyst focused on crypto. I cut through the hype by modeling tokenomics and risk from a purely mathematical standpoint. If the numbers don't work, nothing else matters.
Similar Projects
-
Lightchain AI
Lightchain AI ($LCAI) Review: Tech, Security & Risks 2024
-
Uniswap
Uniswap Review: Scam or Legit Crypto? Complete Legitimacy Analysis
-
DIA
DIA Review: Is This Crypto Project a Scam or Legit? | Scam Check & Legitimacy Analysis
-
DeGuard
DeGuard Review: Is This Web3 VPN Project a Scam or Legit? Crypto Scam Checker
-
Tokuda
Tokuda ($TKD) Review: Assessment of Project Integrity & Risks