Solana Network Outages: A Quantitative Perspective on Stability
Solana's reputation for speed and low fees masks a recurring challenge: outages that disrupt operations across dApps and DeFi. From a quantitative analyst's view, uptime, mean time to recovery (MTTR), and risk concentration matter as much as headline throughput. This article expands the discussion beyond headlines by framing outages in a probabilistic, risk-adjusted lens.
- Overview of Outages
- Causes and Contributing Factors
- Impact on dApps and DeFi
- Risk Metrics and Monitoring
- Best Practices and Mitigation
- FAQ
Overview of Outages
Solana has experienced outages that have lasted from a few hours to several days. The episodes typically follow network upgrades or unexpected surges in activity, testing the system's invariant across validators. From a risk model standpoint, the key question is not only how often outages occur but how quickly the network recovers. Real-time updates are published on the official status hub, Solana Status, which helps researchers gauge time-to-recovery distributions. Additionally, the technical foundation described in Solana documentation clarifies consensus expectations during stress events. For external perspective, coverage such as CoinDesk reporting provides context on market impact.
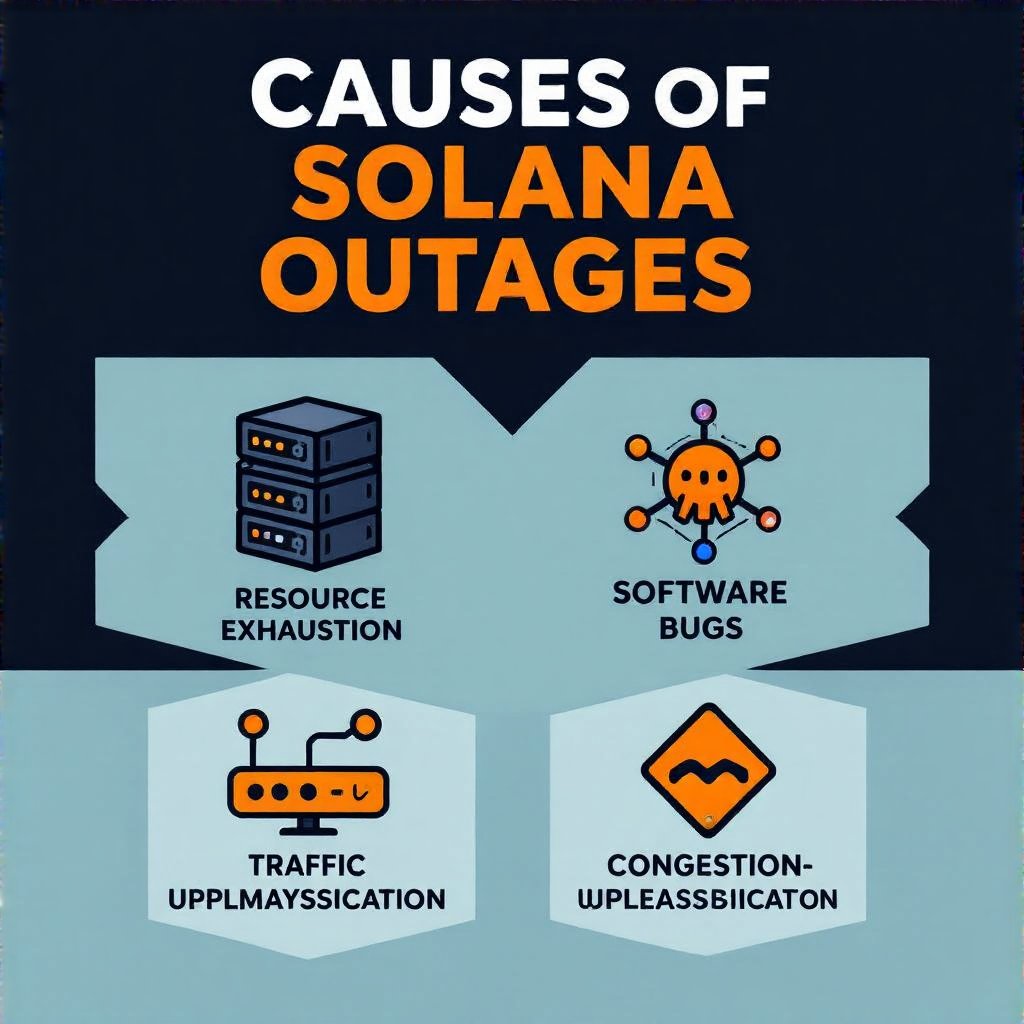
Causes and Contributing Factors
Multiple intertwined factors drive outages:
- Resource Exhaustion: Large bursts in transactions can push validators toward CPU and memory limits, causing slow validation and gaps in finality.
- Software Bugs: Protocol updates may introduce edge cases that disrupt consensus, requiring rollbacks or conservative gating.
- Centralization Risks: A concentration of validators in specific regions or providers can magnify single points of failure during network stress.
- Network Congestion: Sudden demand spikes overwhelm message propagation and block production timelines.
Impact on dApps and DeFi
Outages ripple through the ecosystem. Transactions fail, liquidity pools freeze, and price feeds lag, introducing slippage and increased user frustration. DeFi protocols may experience widened bid-ask spreads and auction volatility, while meme coins can see abrupt price corrections as activity halts disrupt expected flows. For developers, these events raise costs and complicate risk management. See how yield farming risks and other DeFi dynamics relate to outage risk, and how this interacts with tokenomics models like tokenomics to shape incentives.
Risk Metrics and Monitoring
A rigorous approach combines telemetry, governance signals, and market data. Typical metrics include uptime percentage, MTTR, exposure duration, and liquidity resilience. Practitioners compare Solana's profile to peers and consider how cross-chain routing strategies might mitigate exposure by distributing activity across networks. For deeper context on risk-aware analysis, see the discussion on DeFi yield aggregation strategies and the broader tokenomics literature at tokenomics inflation vs. deflation. External monitoring from Solana Status complements internal dashboards, while official docs provide technical guardrails.
| Metric | Solana | Peers |
|---|---|---|
| Uptime (monthly) | Typically ~99.8%, with occasional dips | Often >99.9% |
| Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR) | Hours to days during major events | Typically shorter for well-staffed networks |
| Liquidity Resilience | Varies by protocol and network partition | Often higher liquidity continuity on mature chains |

Best Practices and Mitigation
To navigate outages, teams should implement redundancy, proactive monitoring, and risk-aware deployment. Use validator diversity and diversified RPC endpoints, maintain robust alerting, and conduct simulated outages to validate recovery procedures. Where possible, integrate multi-chain design and cross-chain routing strategies to reduce single-chain dependence. Learn from risk-focused analyses such as yield aggregation patterns and tokenomics insights to align incentives with reliability. For additional context, readers may consult CoinDesk outage coverage.
FAQ
- What defines Solana uptime?
- Uptime reflects the fraction of time validators produce final blocks and services remain reachable.
- Why do outages matter for developers?
- Outages increase costs, reduce reliability, and raise risk premiums for users and lenders in DeFi.
- Can outages be avoided?
- Not entirely, but risk can be mitigated with redundancy, monitoring, and diversified architecture.
- Where can I monitor status updates?
- Official status pages and documentation are the primary sources of truth; see the links above.
