Token Vesting and Locked Liquidity: A Quantitative Lens for Investors

In crypto markets, vesting schedules and locked liquidity are more than compliance features—they are probabilistic levers that shape risk, timing, and potential returns. This article translates hype into a numerical framework, showing how gradual token release reduces supply shocks and how liquidity locks guard against abrupt exits. By combining both tools, investors can estimate expected value with greater discipline than following narrative hype alone.
- What is Token Vesting?
- Why Vesting Matters for Investors
- Understanding Locked Liquidity
- Quantitative View: Risk Mitigation
- Best Practices and Real-World Examples
- Pros, Cons, and Trade-offs
- FAQ
What is Token Vesting?
Token vesting is a schedule that releases tokens gradually over a defined period, preventing founders or early backers from liquidating their entire holdings immediately after launch. The result is smoother price dynamics and more predictable project funding. As CoinDesk notes, vesting aligns incentives for long-term development and investor value.
Vesting timelines vary, but common structures include a cliff (an initial delay before any release) followed by monthly or quarterly vesting. For investors, evaluating the vesting curve—how fast tokens unlock over time—helps estimate supply pressure at each stage of a project’s life cycle. For a broader perspective, see token distribution and vesting schedules.
Why Vesting Matters
- Investor Confidence: Reduces the risk of rug pulls or pump-and-dump schemes by delaying large-scale selling.
- Market Stability: Prevents insiders from flooding the market with tokens too early, which can crash prices.
- Project Credibility: Signals a disciplined development roadmap and measurable milestones.
Understanding Locked Liquidity
Locked liquidity means removing a portion of a project's liquidity tokens from circulation for a defined period or permanently. This is usually enforced by a smart contract and committed to a specific pool or DEX. The lock helps ensure that trading pools maintain adequate liquidity, reducing the risk of sudden liquidity crunches that could be exploited to manipulate prices.
As Cointelegraph explains, liquidity locks are a staple of fair launches and contribute to trust by showing the team cannot drain liquidity at will. For context on how investors assess liquidity safeguards, see also the broader discussions in the linked governance and audit literature.
Beyond immediate price protection, locked liquidity supports market depth and orderly price discovery. It also interacts with vesting to limit both the velocity of token release and the potential for liquidity shortfalls during critical windows of a project’s lifecycle.
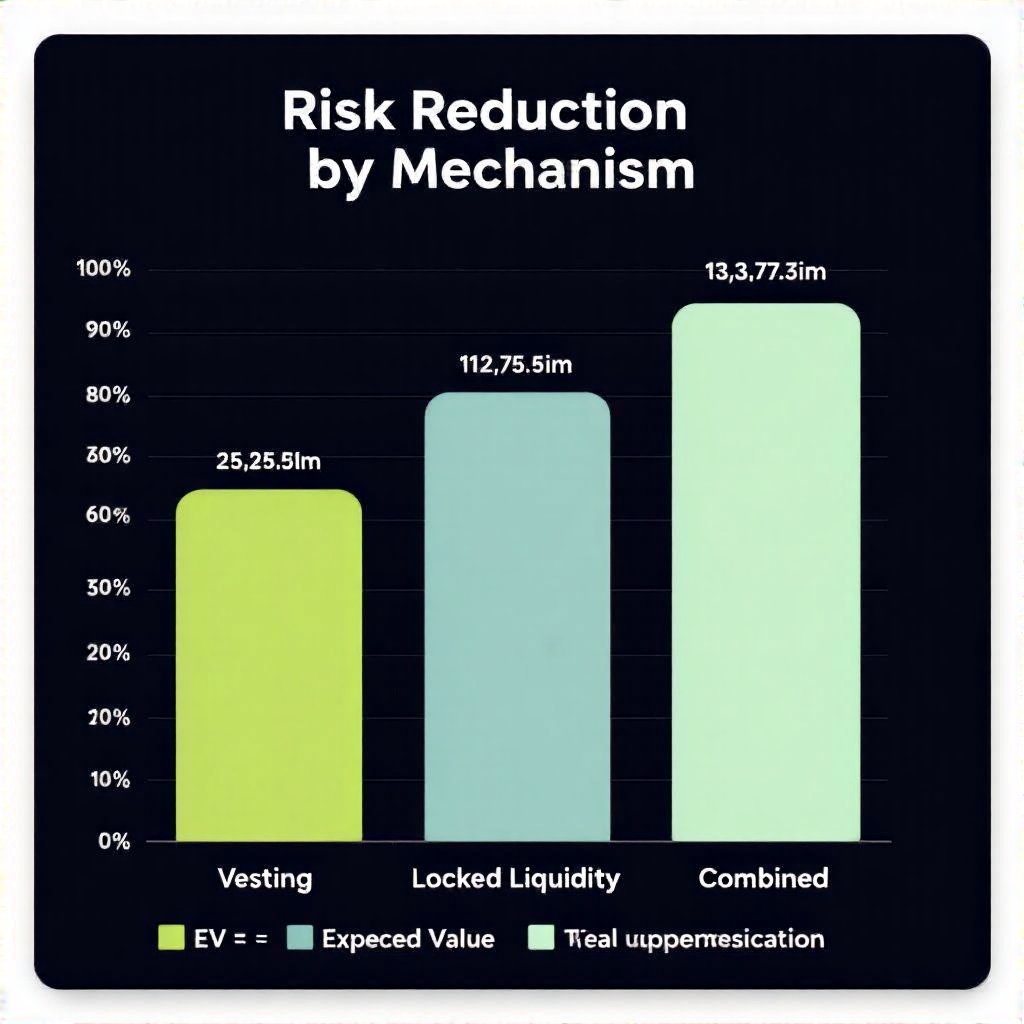
Quantitative View: Risk Mitigation and Expected Value
From a modeling perspective, token vesting reduces supply-side risk by staggering unlock events, while locked liquidity reduces execution risk by preserving pool depth. The combination is not merely additive; it compounds the expected value by lowering the variance of daily returns during early trading days.
Investors should quantify these effects using simple metrics: vesting curve slope, liquidity depth (average pool size), and exit-pressure scenarios. A small illustrative table helps compare scenarios and EV implications. For methodological context, see lossless governance models.
| Scenario | Impact on Risk | Expected Value (EV) |
|---|---|---|
| Vesting only | Moderate risk reduction; delayed supply shock | Lower EV variance |
| Locked liquidity only | Lower price impact on exits; better depth | More stable EV |
| Both together | Significant risk reduction; strongest guardrails | Highest EV certainty |
For deeper methodological guidance, investors may consult partial smart contract audit interpretations and keep an eye on the evolving risk landscape described by CoinDesk.
Best Practices and Real-World Examples
Implementing robust vesting and liquidity locking requires a disciplined framework. Start with clear tokenomics, define cliff and vesting schedules, and publish the timelines to reduce informational asymmetry. AntiShifty’s fair launch principles provide a practical blueprint: a transparent vesting schedule paired with liquidity locks to demonstrate commitment and discourage opportunistic behavior. See fair launch principles.
Other real-world considerations include aligning team incentives with measurable milestones and conducting regular audits to verify that vesting hooks operate as intended. For guidance on evaluating vesting schedules and token distributions, refer to token distribution and vesting schedules.
Pros, Cons, and Trade-offs
Like any mechanism, vesting and liquidity locks carry trade-offs. Vesting reduces liquidation risk but can slow initiative if milestones are missed; locked liquidity can constrain strategic liquidity events in the short term. A balanced approach—combining both tools—often yields the best risk-adjusted outcome for investors, akin to maintaining a diversified portfolio of tokens and liquidity provisions. A quick comparison table below highlights key dimensions.
| Dimension | Vesting | Locked Liquidity |
|---|---|---|
| Timeline control | Yes (cliff + gradual unlock) | Yes (lock duration) |
| Market impact | Reduces new supply shocks over time | Preserves depth during exits |
| Investor confidence | Higher with transparent schedules | Higher with proven locks |
For readers seeking a practical governance lens, see the lossless governance models linked above, and for audits-focused context, explore the audit completeness checks in audit completeness analyses.
FAQ
Q: What is token vesting?
A: A gradual release schedule designed to align incentives and reduce early-dumper risk.
Q: How long should vesting last?
A: Typical ranges run 1–4 years with a 6–12 month cliff; the exact window depends on project maturity and capital requirements.
Q: How does locked liquidity protect investors?
A: Locks prevent abrupt drains of liquidity, supporting orderly trading and price discovery. External coverage on fair launches provides additional context.
Q: Where can I learn more about complete audits?
A: Review the audit scope and maturity, and consult interpretations such as partial audit interpretations for broader risk awareness.

