Ensuring Solana Token Metadata Integrity

In Solana, token metadata attaches to tokens via the Metaplex standard, shaping how wallets display names, symbols, and URIs. The integrity of this data is critical for trust and interoperability across wallets and dApps. A small mismatch can ripple through explorers, wallets, and dApps, creating mispricing or fraud signals.
On-chain and off-chain data must be synchronized. The URI field points to JSON that describes the asset; keeping that data accurate and verifiable is a cornerstone of reliable token ecosystems.
- Solana Token Metadata Basics
- IPFS Role in Metadata Management
- Risks of Mutable Metadata
- Best Practices for Integrity
- Security and Auditing
Solana Token Metadata Basics
Tokens carry data fields such as name, symbol, and a URI that points to off-chain data. The Metaplex standard governs this structure (Metaplex docs). The data's accuracy affects user experience and audits. For a deeper dive into asset security, see Understanding Smart Contract Vulnerability Exploitation in DeFi.
The mapping between on-chain metadata and off-chain JSON must be stable. Servers and pinning strategies should ensure that the same URI resolves to the same content across clients and time.
IPFS Role in Metadata Management
IPFS provides decentralized storage for metadata, improving accessibility and resilience. However, IPFS links can be mutable if not pinned and versioned correctly. See IPFS docs for best practices. You can also audit this architecture with methodologies from Red4Sec Audit Methodologies & Best Practices for Crypto Security.
Performance matters: metadata JSON should be compact, and the hosting strategy should balance speed with availability. Use content-addressable hosting and efficient caching to keep wallets responsive while preserving integrity.
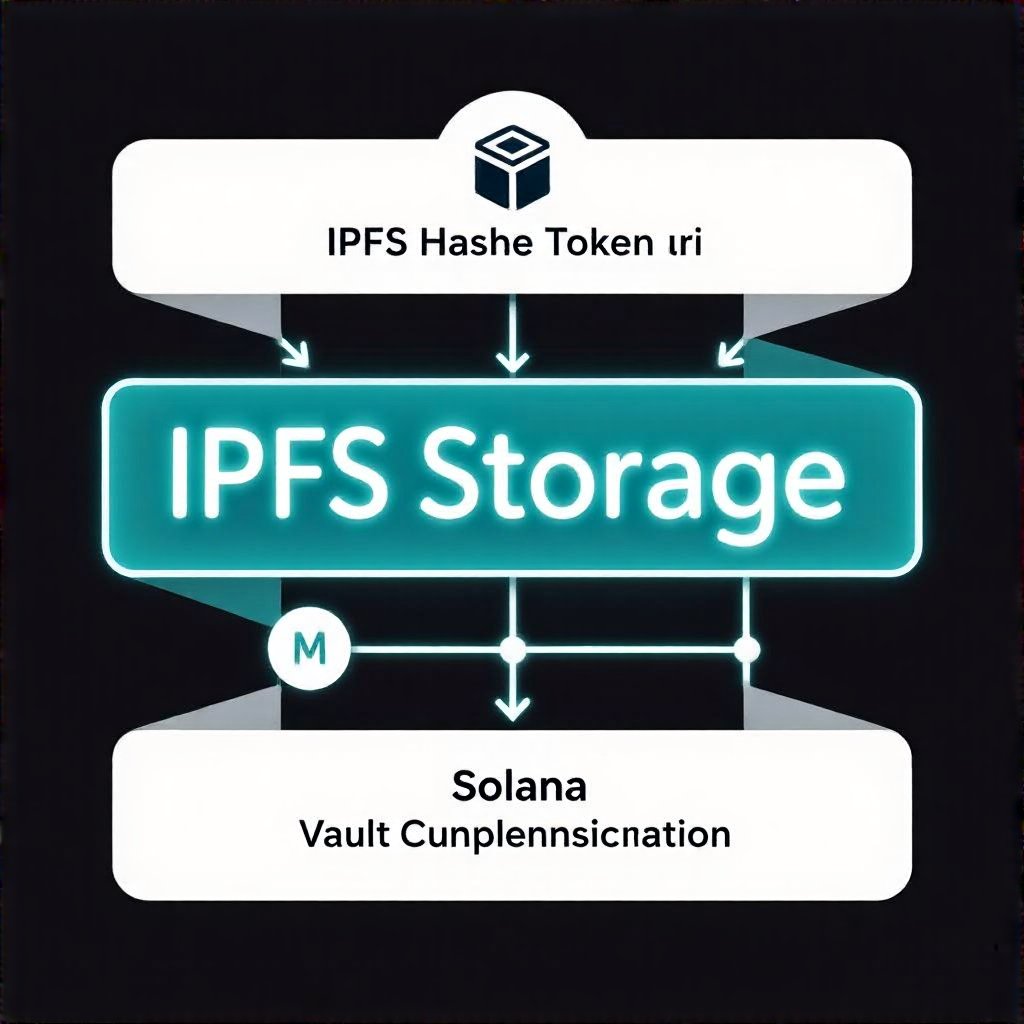
Risks of Mutable Metadata
Mutable data can be changed by control of the source or compromise of the storage bridge. This risk undermines user trust and can affect token economics. It creates exposure to attacker-controlled URIs, tampered JSON, or delayed revocation signals. The community increasingly emphasizes immutable pointers, content verification, and auditable provenance.
Best Practices for Integrity
- Use versioned metadata and signed manifests to track changes over time.
- Pin and verify IPFS objects with multiple gateways and hash checks to prevent single points of failure.
- Audit your workflow with recognized security firms such as SlowMist Audit Methodology and Red4Sec Audit Methodologies.
Security and Auditing
Security is a data integrity issue as much as a code issue. Regular threat modeling, version controls for metadata files, and cryptographic signing help prevent unauthorized changes. Audits from established firms provide a structured assessment of controls around issuance, updates, and revocation. See the two audit frameworks above for practical templates and checklists.

